Osteonecrosis is the cause of acute back pain in 67% of all cases. Failure to receive timely advice, consultation and treatment from a doctor can lead to consequences such as dysfunction of internal organs, damage to the spinal cord and damage to the nerve roots of the spine. What is osteoarthritis, what treatments are available to patients and how to diagnose the disease - read on.
What is osteonecrosis?
Chondrolysis is a degenerative-dystrophic disease that leads to thinning of cartilage between vertebrae. The hyaline cartilage and intervertebral discs begin to "wear out", losing their ability to function fully.
Authority to solve.In most cases, spondylosis is diagnosed in people 25 years of age and older. According to WHO, as of 2021, 43% of the population aged 25-40 will have osteochondrosis and more than 92% of people in old age. The appearance and exacerbation of the disease can be caused by surrounding adverse factors.
Types of osteoarthritis
Every part of the spine is subject to degeneration. Among the types of osteoarthritis of the spine, 3 main types can be distinguished: cervical, thoracic and lumbar (due to heavy loads, it is more common than other types).
- Lumbar bone degeneration.The lumbar region consists of 5 vertebrae that are easily deformed due to the negative effects of external and internal factors. When the nutritional and metabolic processes in the disc are interrupted, pain will occur due to loss of elasticity and thinning of cartilage tissue.
- Cervical bone degeneration.The cervical spine consists of 7 vertebrae that are constantly under pressure. Pathological processes are triggered when the body's metabolism fails.
- Osteoarthritis of the chest.The thoracic region includes 12 vertebrae. This type of osteonecrosis is the least common. The thoracic vertebrae do not function. People who lead a passive lifestyle and often lift heavy objects are susceptible to the disease.
Causes of osteoarthritis
The number of people with osteoarthritis is increasing rapidly every year. This is due to the fact that people spend most of their time on their feet, providing maximum load to the intervertebral discs.
Important!With age/due to heavy loads, the intervertebral disc and cartilage become deformed. Clefts and hernias may appear. As a result, nerve roots are compressed, intervertebral discs thin out, pathological processes in the spinal cord, muscle spasms and pain increase.
Risk groups include: office workers, construction workers, hairdressers, salespeople, drivers. Both men and women are equally susceptible to osteoarthritis.
Factors that stimulate cartilage degeneration include:
- presence of osteoarthritis in family history;
- overweight, obesity;
- passive lifestyle;
- flat feet.
Degeneration of the spine and its deformity can be caused by the following factors:
- Self-neglect (complete lack of physical activity or excessive exercise).
- Lack of awareness of correct postures to reduce stress on the spine.
- Work that continuously involves lifting/moving heavy objects.
- Injury.
Osteonecrosis: 4 stages of disease development
There are 4 stages of development of spondylosis:
- Early stage- There are no clear symptoms to diagnose the disease. Back pain occurs occasionally, usually after exertion or overexertion. Osteoarthritis in the early stages can be detected during preventative examinations or during CT scans or X-rays.
- Second stage.The next stage is characterized by moderate pain. Cartilage tissue begins to deform and the space between spinal discs gradually decreases. When contacting a doctor, drug therapy (for pain relief) and physiotherapy are prescribed.
- Third stage– The spine is deformed, fibrous areas and hernias appear, the pain becomes more intense and more frequent. At this stage, everything depends on the existing symptoms. The doctor will help determine the patient's treatment method (conservative or surgical).
- Fourth stage- Irreversible deformation of spinal function. The patient is almost unable to move independently. The pain is acute, constant and increases with physical activity. Pathological bone tissue fills the intervertebral space, the patient becomes disabled.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis
As mentioned earlier, there are 3 types of osteoarthritis and each type is characterized by individual manifestations. Let's look at all the symptoms further.
Symptoms of lumbar osteoarthritis
How to understand that you have lumbar osteoarthritis? You may notice characteristic symptoms:
- stiffness of movement;
- pain in the pelvis, sacrum, lower back and lower limbs, which becomes more intense with exercise or movement. The nature of the pain is aching, dull, sharp;
- pathological processes of the genitourinary system (problems with defecation and urination);
- weakness in the legs;
- impaired/lack of sensitivity.
Important!Self-medication is strictly prohibited. When lumbar osteoarthritis is detected, effective diagnosis and treatment are mandatory. The consequences of lack of treatment are hernias, protrusions, and paralysis of the lower limbs.
Symptoms of cervical spondylosis
How to understand that you have cervical spondylosis? One or more symptoms may occur:
- Frequent headaches;
- numbness in the upper and lower limbs;
- Severe cracking sounds in the cervical spine during physical activity;
- "spots", eye dots, cloudy and dark;
- burning sensation and discomfort in the heart area;
- the appearance of tinnitus, hearing loss;
- unexplained dizziness;
- pain in shoulders, neck, arms.
Important!Cervical spondylosis is considered one of the most dangerous diseases for humans, because it complicates the process of blood saturation in the brain. If left untreated, protrusions appear followed by hernias. Surgical intervention to treat cervical spondylosis has a high risk of causing body paralysis. If symptoms appear, contact only qualified professionals.
Symptoms of breast osteonecrosis
How to understand that you have thoracic osteoarthritis? Only a doctor (neurologist) can diagnose the disease, but the patient can assume the presence of osteoarthritis based on characteristic signs:
- discomfort, local burning sensation in the chest;
- Pain appears when raising arms, pain in shoulder blades;
- sudden dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- chest pain.
Authority to solve.As the disease progresses to the acute stage, dorsago (lack of air, sharp/hard pain in the chest, "lumbar pain") and back pain (pain can be episodic or continuous, acute/dull in nature) can happen.
Osteonecrosis of the thoracic spine is difficult to diagnose. The disease is often confused with angina, heart attack or inflammatory processes in the lungs.
Diagnosis of spondylosis
When you see your doctor, your medical history and physical examination of the musculoskeletal system will begin.
patient equipment. The specialist will check the integrity of reflexes and the sensitivity of the painful area. Then, blood tests and other laboratory tests will be ordered. To clarify the diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes one or more types of imaging:
- Ultrasound of the vertebral artery.
- X-ray of the entire spine or certain areas (neck, chest, lumbar).
- CT scan of the spine helps determine the presence of degenerative processes, displacement, and deformation of the spine and its structures.
- Spinal MRI - identifies soft tissue pathologies, helps scan the spinal cord and intervertebral discs.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
The way to treat osteoarthritis is determined by the attending physician, depending on the type of disease, the severity of symptoms and the degree of pathological changes. The following can be used as therapy: physical therapy, drug treatment, classes with a chiropractor, therapeutic massage, therapeutic exercise, or surgical intervention(in the absence of positive momentum from other treatments or at an advanced stage).
Medicines to treat osteoarthritis
When prescribing medical treatment with drugs, doctors can use multiple groups of drugs at the same time:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) - to relieve osteoarthritis symptoms, relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Can be used in pill form or injection form (in severe cases). The duration of the treatment course is from 7 to 14 days;
- chondroprotectors – to strengthen intervertebral discs and cartilage tissue;
- B vitamins;
- Vascular drugs - to improve blood supply to the spine;
- glucocorticosteroid – administered as an injection into the affected area (for severe forms of the disease);
- muscle relaxants - to relax muscles, reduce pain and inflammation.
Massage to treat osteoarthritis
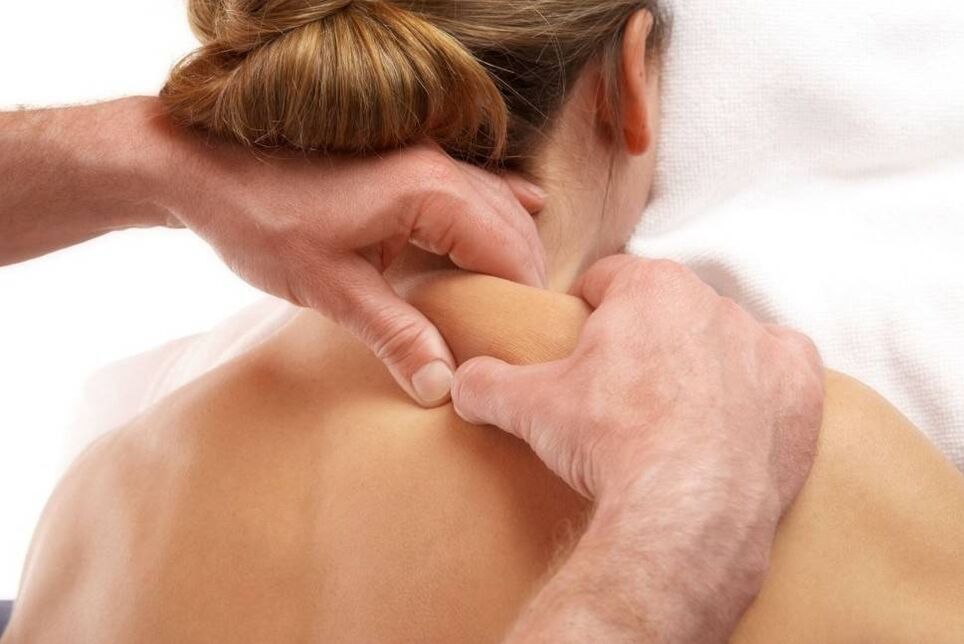
An osteoarthritis massage course must be completed every six months. Massage therapy helps eliminate tension, reduce stress and improve blood circulation in the affected area. Only a doctor can speak about the advisability of prescribing massage, the prerequisite of which is remission of the disease.
Traction (spinal traction)
Artificial traction of the spine is performed only under the supervision of medical personnel, using special equipment. High-quality traction allows you to evenly distribute the vertebrae in the spine. Pain, pinching and inflammation are reduced.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy for spondylosis is used to correct the curvature. The specialist applies targeted impact on the patient's musculoskeletal system. After treatment, blood and lymph circulation improves, joint stiffness disappears, and mobility appears.
Physical therapy treatment of osteoarthritis
It is carried out only during periods of remission of the disease; in the acute stage, this method of treatment is prohibited. Physiotherapy is used as an auxiliary therapy, along with drug treatment. To reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis, experts use lasers, magnets and electric currents (low frequency).
Acupuncture
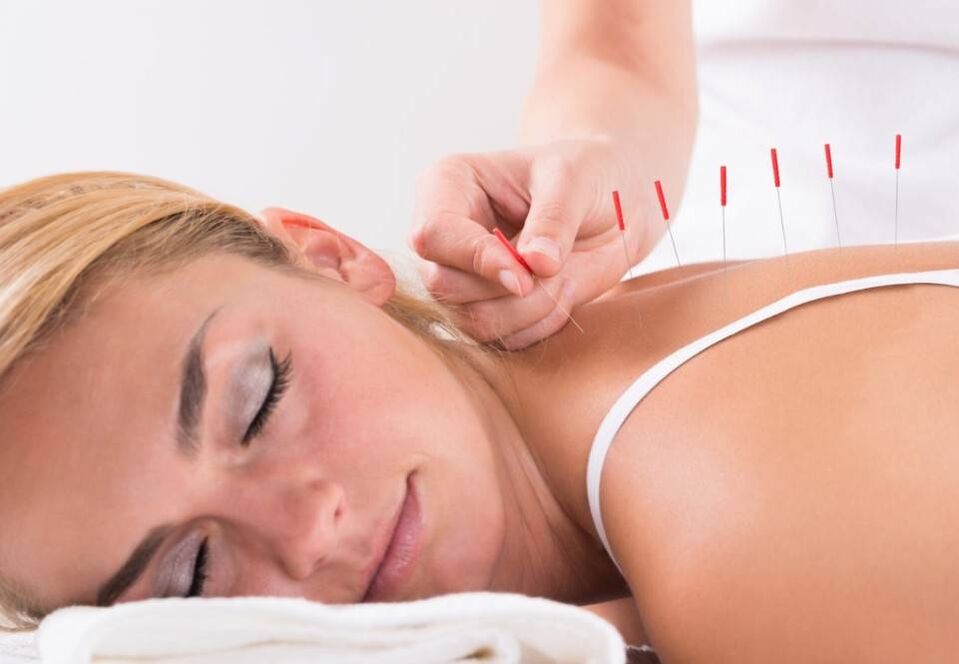

The basis of acupuncture is the precise impact on reflex zones and pain points. Therapy is only indicated in combination with massage therapy to increase effectiveness. This therapy restores the natural load-bearing capacity of the spine without causing pain.
Exercise therapy for osteoarthritis
Physical therapy is effective for all types of osteoarthritis and can be prescribed to patients of all ages. The type of exercise and duration are prescribed by your doctor. Moderate physical activity helps strengthen back muscles, increase mobility and flexibility of the spine, and improve the patient's condition.
Patients may be assigned the following types of classes: occupational therapy, therapeutic swimming, health pathways, occupational therapy.
Important!Exercise therapy classes are contraindicated during periods of exacerbation of osteoarthritis!
Surgery to treat osteoarthritis
For osteoarthritis of the spine, surgery is rarely indicated as the only treatment option. The human spine has a complex structure with many vertebrae and nerve endings that affect the coordinated functioning of the entire body. Surgery has a high risk of complications so is only indicated in the most difficult cases or when other treatments fail to improve the condition.
Preventing bone degeneration of the spine
Prevention is the best way to reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis and achieve remission for existing spinal disease. The main thing to remember when performing preventive exercises is that they should be regular and only during periods of relief.
It is better to do a series of simple exercises at the same time. To avoid forgetting them, set reminders on your cell phone or incorporate them into your morning hygiene rituals.
- Place your forehead in your palm, tense your neck muscles. Perform – 3 rounds, each round 5-7 seconds. Then repeat the same with the back of the head and palms.
- The position of the shoulders is level, the head is straight. Slowly tilt your head as far as possible to the right, then to the left. Do it 5 times (slowly).
- Slowly tilt your head back a little. Tighten your neck muscles and gradually move your chin toward your chest. Do 5-7 times.
- Place your left palm near the left temple area (then the right palm and right temple). Apply pressure to your palms, stretching your neck muscles. Do – 3 times in 10 seconds.

Important!Don't rush when doing the exercises. Making circular movements with the head is also prohibited due to the high risk of injury and compression of nerve endings.
The second set of preventive exercises against osteoarthritis can be done at any time (especially after work or overexertion), but also regularly:
- Stand straight, legs together, arms relaxed, take a deep breath. Raise your hands, exhale. Approach – 6-8 times.
- Lie on your stomach, arms along your body, relax. Bend up, put your hands up, try to lift your head and legs. Hold this position for 5 seconds. Return to starting position. Repeat - 5 - 7 times.
- Sit down in a chair. Place your hands behind your head (inhale deeply), bend back 4-5 times so that your shoulder blades touch the back of the chair (exhale). Repeat - 5 - 7 times.
- Stand up, bend over, take a deep breath. Relax your arms, lean forward, slowly lower your head and shoulders - exhale. Approach – 10 times.
- Get on all fours. Go straight. Arch your back and hold this position for 3-4 seconds. Return to starting position, repeat 5-7 times.
How to stand, lie down and sit when you have osteoarthritis?
Knowledge of correct postures that distribute the load evenly over the entire spine is necessary not only for patients with osteoarthritis, but for everyone. By following simple rules, you will notice a significant improvement in your general condition and reduce the load on your back. Additionally, you can protect your spine from many diseases with severe, painful symptoms.
How to sit correctly?
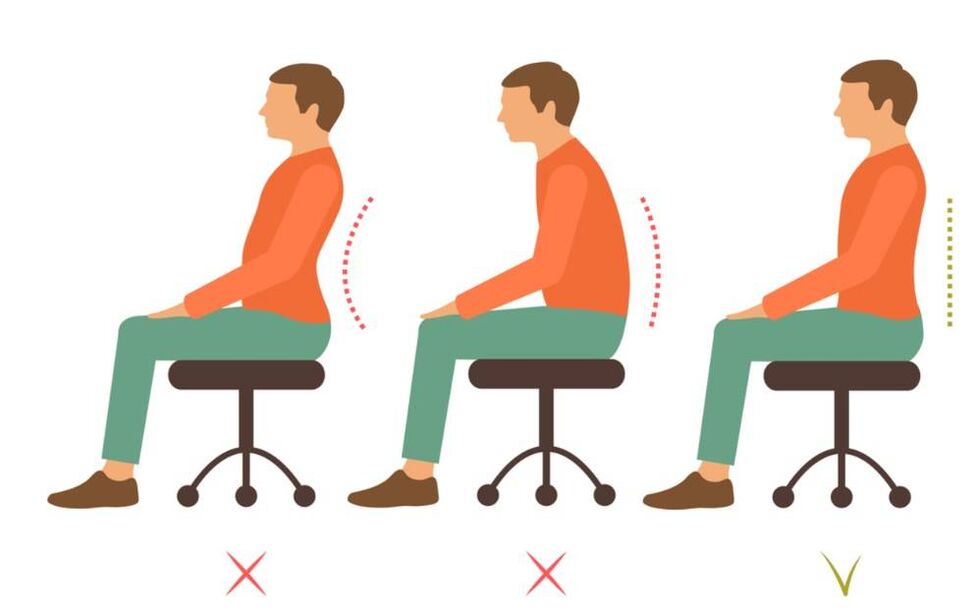
We learn to sit without pressure, without risking spinal deformity and developing osteoarthritis:
- Criteria for choosing a chair/seat: seat depth - 2/3 of the length of the hips, seat height must be equal to the length of the lower leg. This way, your feet will stay on the floor. Small people need to put a small step or a bench under their feet;
- Pay attention to the depth of the desktop. It must be such that the legs do not need to be placed to the side or bent sharply;
- When sitting for long periods of time, take a break every 20 minutes. Change the position of the legs, walk, do light exercise;
- Get behind the wheel with minimal stress. Your back should rest against the chair; a small pillow or cushion placed between the chair and your lower back will help with this. If possible, get out of the car every 25-30 minutes to warm up;
- Thick upholstered furniture is not good furniture for everyday use. For an even load on the spine, it is necessary to support the body on the ischial tuberosities, which can only be done when sitting on a surface of moderate hardness;
- Your back should always touch the back of the chair/work chair. Try to sit up straight, avoid bending your neck too much;
- Do not sit/lie in one position for long periods of time.
How to stand correctly?
If a person stands in one position for a long time, a large load will be placed on the lumbar region (and the entire spine), which will negatively affect it. To avoid putting too much pressure on the spine and increasing the risk of deformity, follow these simple rules:
- Do not stand in one position for more than 10 minutes, change the position of your legs and arms;
- relieve tension in the neck - tilt your head to the right and left, stretch your arms forward, bend your back forward and backward - relax your back and lower back;
- When lifting something off the floor, bending over, bending your knees, or squatting, find support for your hands;
- move, walk short distances so as not to stand still;
- Try not to bend down too much (back, head) when doing housework (cleaning, ironing, cooking). When cleaning low or hard-to-reach surfaces, get down on one knee.
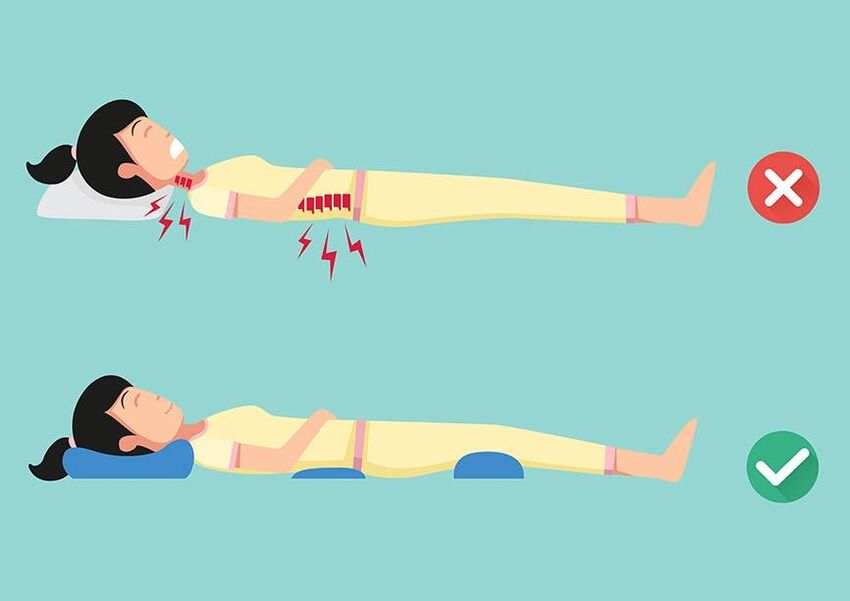
How to lie down?
The ideal sleeping surface choice is a bed with a mattress of moderate firmness (ideally an orthopedic mattress that helps maintain the physiological curve of the spine). The bed should not be wooden or too soft.
How to lie down properly if you have severe pain?
- back pain - lie on your stomach, put a small pillow under the lower back (so as not to increase the pain when bending over);
- pain in the legs - put a cushion (from a towel or blanket) under the knee. Pain syndrome will gradually decrease;
- neck pain - place your hands under your head or cushion under your neck.
How to get out of bed in the morning when osteoarthritis attacks?
- perform a short warm-up for the upper and lower limbs;
- change your location;
- move from a lying position to a sitting position, hugging your legs, arms bent at the knees;
- lower each leg to the floor;
- Get up gradually; any sudden movements can increase the pain.
How to lift and move weights properly?
Improper lifting and carrying heavy objects is one of the most common causes of hernias, osteoarthritis and bone protrusions. Sudden lifting of weights can cause sudden "shooting" of different parts of the spine and the appearance of prolonged acute pain. Turning while carrying heavy objects is also prohibited.
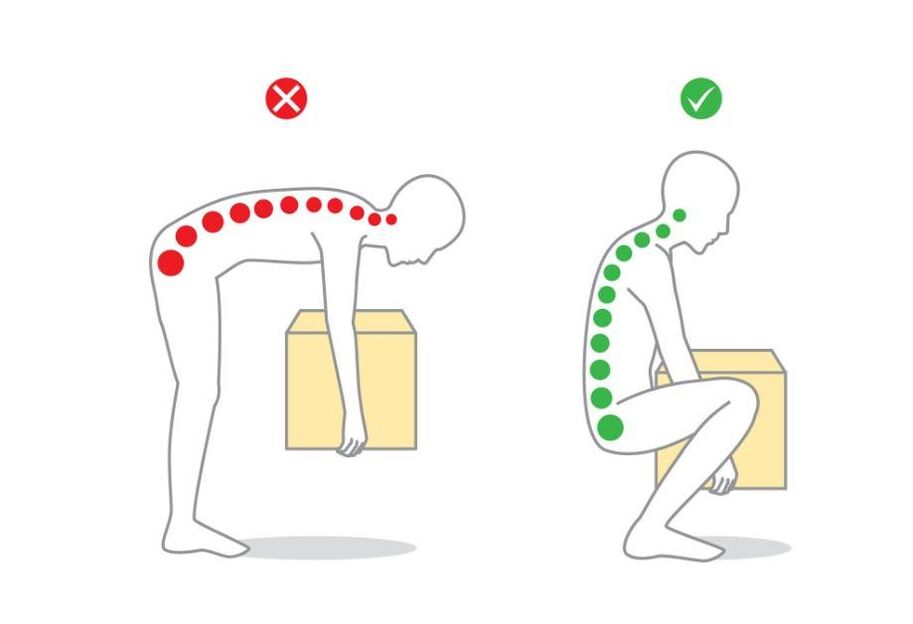
How to lift a heavy object?
- Wear a wide belt.
- Squat down. Keep your neck and back straight.
- Secure the object with both hands, stand up slowly, keeping your back straight.
How to move a heavy object?
- distribute the load evenly on both hands, do not carry everything in one hand;
- With diagnosed osteoarthritis, it is not recommended to lift objects weighing more than 15 kg;
- buy a backpack (important conditions are an orthopedic back and wide straps). The advantage of using a backpack is an even load on the spine + free hands;
- Do not lean forward or backward suddenly.
Conclusion
Spondylosis most often develops between the ages of 25-40. The risk group for the disease includes people leading a passive lifestyle, those who spend most of their time standing or in incorrect posture, subjecting large loads to the spine. Osteonecrosis can be cured by conservative methods, requiring timely consultation with a specialist. In advanced cases, surgical intervention is used. Self-medication is contraindicated.
Regular preventive exercises will help reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis and maintain the function of the spine, protecting against deformity. If you neglect your health, you can delay seeing a doctor until hernia, paralysis and disability occur.